1. Process route
The production technology of dichloroethane can be divided into ethylene direct chlorination method and ethylene oxychlorination method
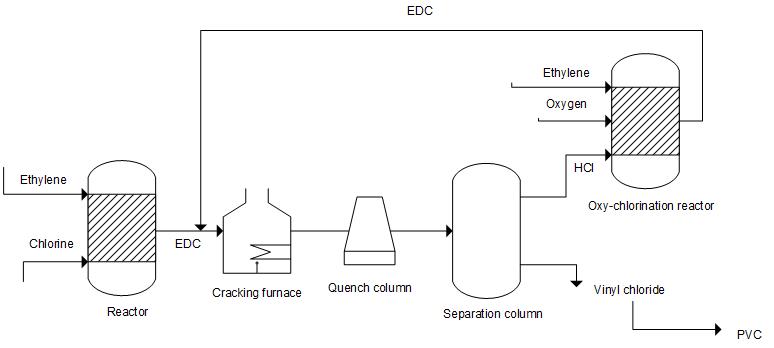
(1) Ethylene is directly chlorinated to produce dichloroethane (EDC), which undergoes a chlorination reaction with chlorine gas to produce dichloroethane. dichloroethane is cracked to produce vinyl chloride (VCM), and vinyl chloride is polymerized to produce polyvinyl chloride (PVC);
(2) Ethylene is directly chlorinated to produce dichloroethane (EDC). Ethylene, hydrogen chloride, and oxygen undergo an oxychlorination reaction to produce dichloroethane, which is then cracked to produce vinyl chloride (VCM) and polymerized to produce polyvinyl chloride (PVC);
(3) Equilibrium method vinyl chloride is a byproduct of direct chlorination in the production of DEC cracking VCM. Hydrogen chloride is generated again through ethylene oxychlorination to generate EDC, and dichloroethane is further cycled for cracking to generate VCM. By matching, a closed-loop production can be achieved.
The reaction equation is as follows:
①C2H4+Cl2 → CH2ClCH2Cl
②CH2ClCH2Cl → CH2CHCl+HCl
③2HCl+C2H4+O2 → CH2ClCH2Cl+H2O
④nCH2=CHCl → (-CH2CHCl-)n
2. Process flow
3. Technical advantages
The ethylene oxychlorination process technology package independently developed by Shandong Jereh Catech Technology Co., Ltd. uses domestic catalysts and achieves complete localization of the process technology, greatly reducing production costs and promoting the development of the domestic vinyl chloride industry. Catech Technology's technology can efficiently treat by-product hydrogen chloride, achieve chlorine balance, and has advantages such as high product purity, low three wastes, excellent performance, and high price.
4. Downstream market direction
① Dichloroethane → Organic solvents and extractants;
② Dichloroethane → Trichloroethane;
③ Dichloroethane → vinyl chloride → polyvinyl chloride.






 中文
中文



